Allergic reactions are the body’s response to substances it perceives as harmful, known as allergens. These reactions, which can be triggered by a variety of factors, vary significantly in severity. This variability is not only observed in different individuals but can also occur within the same person at different times, reflecting the complex nature of the immune system’s response to perceived threats.
Common Triggers of Allergic Reactions
Food Allergies
Food allergies occur when the immune system mistakenly targets a harmless food protein — an allergen — as a threat.
- Nuts: Both peanuts, which are legumes, and tree nuts like almonds, cashews, and walnuts can trigger severe allergic reactions.
- Seafood: Shellfish, such as shrimp, lobster, and crabs, and fish like salmon or cod can cause serious reactions.
- Dairy: Milk allergies are most common in children and can include reactions to cow’s milk and milk products.
- Eggs: Both the egg whites and yolks can be allergenic, although most reactions are typically associated with the proteins in egg whites.
Drug Allergies
Allergic reactions to medications, whether prescription or over-the-counter, can occur in some individuals.
- Penicillin and Related Antibiotics: One of the most common drug allergies, reactions can range from rashes to anaphylaxis.
- Aspirin and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Anti-inflammatory drugs can cause a variety of allergic responses, including respiratory issues, particularly in individuals with asthma.
- Other Medications: Local anesthetics, anticonvulsants, and some contrast dyes used in imaging tests can also cause allergic reactions.
Insect Stings
Allergies to insect stings can be particularly dangerous and potentially life-threatening.
- Bees and Wasps: Wasp and bee stings inject venom that can trigger allergic reactions in some people, ranging from local pain and swelling to severe systemic responses.
- Fire Ants: Stings from these insects can also cause allergic reactions similar to bee and wasp stings.
Environmental Allergens
Substances found in our everyday environment can cause allergic reactions, particularly affecting the respiratory system.
- Pollen: Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds is a common cause of allergic rhinitis or hay fever.
- Pet Dander: Proteins found in the skin flakes, urine, and saliva of furry pets like cats and dogs can trigger allergic reactions.
- Dust Mites: Microscopic creatures known as “dust mites” thrive in household dust and can cause year-round allergies and asthma.
Symptom Analysis and Identification
Allergens and their sources can vary widely, and each person reacts differently, which can cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe and even life-threatening. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for timely and appropriate response.
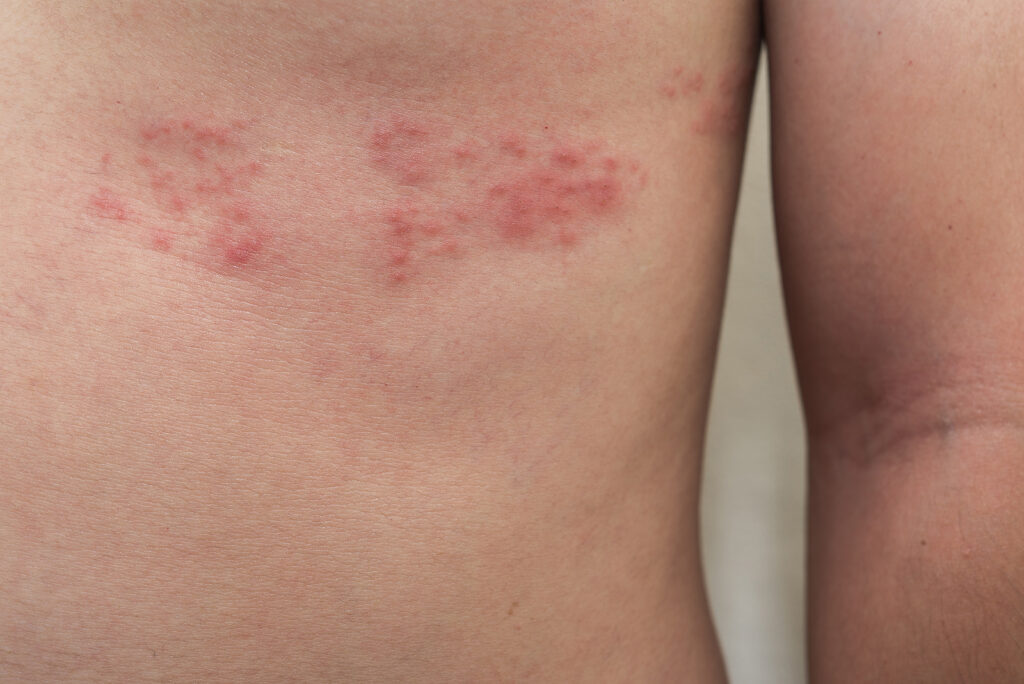
Skin Reactions
- Hives: These are red, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body. Hives are often the body’s response to allergens and can vary in size.
- Itching: This is a common allergic symptom, often occurring without visible skin changes. Itching can be localized or widespread.
- Eczema: This condition is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It’s often seen in people with a history of food allergies.
Respiratory Symptoms
- Sneezing: Often accompanied by a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing is a common response to airborne allergens.
- Nasal Congestion: Swelling of the nasal passages can occur when someone is exposed to allergens, making breathing through the nose difficult.
- Coughing and Wheezing: These symptoms may indicate allergic asthma or a reaction affecting the lower airways.
- Difficulty Breathing: This can be a sign of a more severe reaction, especially if it occurs suddenly and is accompanied by other symptoms like wheezing.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can occur as the body’s reaction to ingested allergens.
- Diarrhea: Allergic reactions affecting the digestive system can result in diarrhea.
- Abdominal Pain: This can be a result of swelling or spasms in the digestive tract in response to allergens.
Severe Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
Anaphylaxis is the most severe form of allergic reaction and requires immediate medical attention.
- Difficulty Breathing: This can be due to swelling of the airways, making it one of the most dangerous symptoms of anaphylaxis.
- Swelling of the Throat or Tongue: Known as angioedema, this can rapidly worsen and obstruct the airway.
- Sudden Drop in Blood Pressure (Hypotension): This can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting, indicating a severe systemic reaction.
- Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases, a person may lose consciousness due to decreased blood flow to the brain.
- Other Symptoms: There can be rapid heartbeat, confusion, or a severe headache.
Recognizing these symptoms promptly and responding appropriately can be the key to effective treatment, especially in the case of severe reactions like anaphylaxis.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Reactions
At Elitecare Emergency Hospital, our approach to allergic reactions includes immediate assessment and swift intervention.
- Immediate Medical Assessment: Our team promptly evaluates the severity of the reaction, considering the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
- Diagnostic Testing: Skin tests or blood tests can be employed to identify specific allergens, especially in cases of recurrent or unclear allergic reactions.
- Emergency Treatment for Severe Reactions: In cases of anaphylaxis, immediate care is critical, followed by continuous monitoring and supportive care.
- Medication Management: For less severe reactions, treatment may include medications to alleviate symptoms.
- Continuous Monitoring and Care: For conditions requiring ongoing observation, our facilities are equipped to provide continuous care, ensuring your stability and recovery.
- Patient Education and Prevention: We provide guidance on avoiding known allergens and managing reactions, including the proper use of epinephrine auto-injectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: When should I seek emergency care for an allergic reaction?
A: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms of anaphylaxis, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid drop in blood pressure. For less severe reactions, consult with a health care provider for appropriate management.
Q: Can allergic reactions become more severe over time?
A: Yes, the severity of allergic reactions can change over time. A mild reaction in the past does not guarantee that future reactions will be mild.
Q: How can I identify my allergy triggers?
A: Identifying triggers often involves a combination of reviewing your medical history, observing when reactions occur, and potentially undergoing allergy testing.