Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, causing a number of symptoms that can have a huge effect on the affected person.
The severity of pneumonia can range from mild to life-threatening. It is most serious for infants and young children, people older than 65, and those with health problems or weakened immune systems.
Understanding the different causes, symptoms, and treatment options is a must for effective management and recovery from this condition.
Common Types of Pneumonia
- Bacterial Pneumonia: This is the most common type of pneumonia. The most frequent cause is the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. Other bacteria, such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydophila pneumoniae, can also cause pneumonia.
- Viral Pneumonia: Respiratory viruses, including influenza (the flu), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19), are common causes of pneumonia, particularly in children and the elderly.
- Fungal Pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is most common in individuals with chronic health problems or weakened immune systems. Fungi from soil or bird droppings can cause pneumonia, especially in certain geographic regions.
- Aspiration Pneumonia: This happens when food, saliva, liquids, or vomit is breathed into the lungs or airways leading to the lungs. This often occurs in people with impaired gag reflexes or those under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Symptom Analysis and Identification
- Cough: A persistent cough that may produce phlegm (mucus) is one of the most common signs of pneumonia. The phlegm may be greenish, yellowish, or even bloody.
- Fever and Chills: Pneumonia often causes a fever, which may be accompanied by shaking chills. The fever can range from mild to high.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or rapid, shallow breathing can occur, often becoming more pronounced with exertion.
- Chest Pain: Sharp or stabbing chest pain that worsens during deep breaths or coughing is a common symptom.
- Fatigue and Weakness: People with pneumonia often experience general weakness and fatigue, which may persist even after other symptoms have subsided.
- Other Symptoms: Additional symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and confusion (especially in older adults).
In children, the symptoms of pneumonia can be less specific and may include irritability, lethargy, and difficulty feeding. Infants might have a lower-than-normal temperature rather than a fever.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pneumonia
The treatment approach for pneumonia is determined based on the patient’s age, overall health, and the severity of the disease. Early and appropriate diagnosis is crucial for a full recovery.
- Medical History and Physical Examination: The diagnosis process begins with a review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms, followed by a physical exam. During the exam, the doctor listens to the patient’s lungs with a stethoscope.
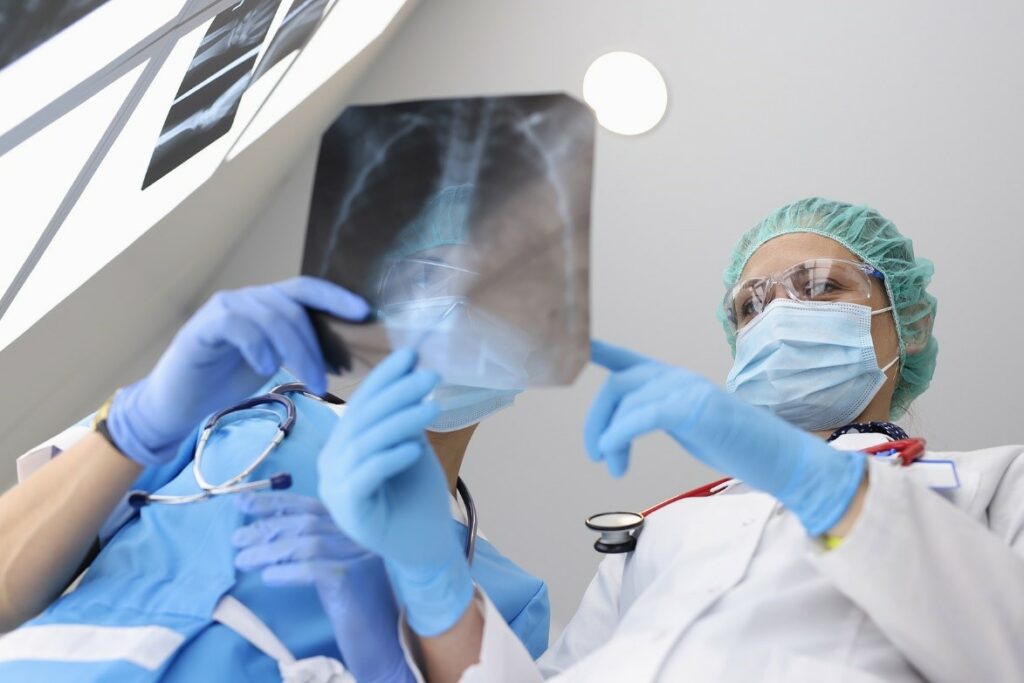
- Chest X-ray: This is a key diagnostic tool for detecting pneumonia and determining its extent and location in the lungs.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to confirm an infection and to try to identify the organism causing the infection, although this is not always possible.
- Sputum Test: Analysis of sputum (the mucus coughed up from the lungs) can sometimes reveal the cause of the pneumonia.
- Pulse Oximetry: This test measures the oxygen level in the blood and can help determine how severe the pneumonia is.
- Antibiotics: If pneumonia is caused by bacteria, antibiotics are prescribed. It’s important to take the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if the patient starts feeling better.
- Fever Reducers/Pain Relievers: Medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to reduce fever and alleviate pain.
- Rest and Fluids: Adequate rest and staying well-hydrated are important in helping the body recover.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I differentiate pneumonia from a common cold or flu?
A: While colds and flu can share some symptoms with pneumonia, such as cough and fever, pneumonia symptoms are typically more severe. Pneumonia often involves a deep cough that produces phlegm, high fever, sharp chest pain, and pronounced difficulty breathing.
Q: Is pneumonia contagious, and how is it spread?
A: Pneumonia itself is not contagious However, the germs that cause pneumonia, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi, can spread from person to person. Transmission usually occurs through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing.Good hygiene practices, like regular hand washing and covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing, can help prevent the spread.
Q: Can I prevent pneumonia?
A: Yes, there are several ways to reduce the risk of getting pneumonia. These include getting vaccinated (pneumococcal vaccines and annual flu shots), practicing good hygiene, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking.
Get the Care You Need
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms that suggest pneumonia, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
At Elitecare, we provide comprehensive care for pneumonia, including accurate diagnosis and effective treatment tailored to each patient’s needs, 24/7.