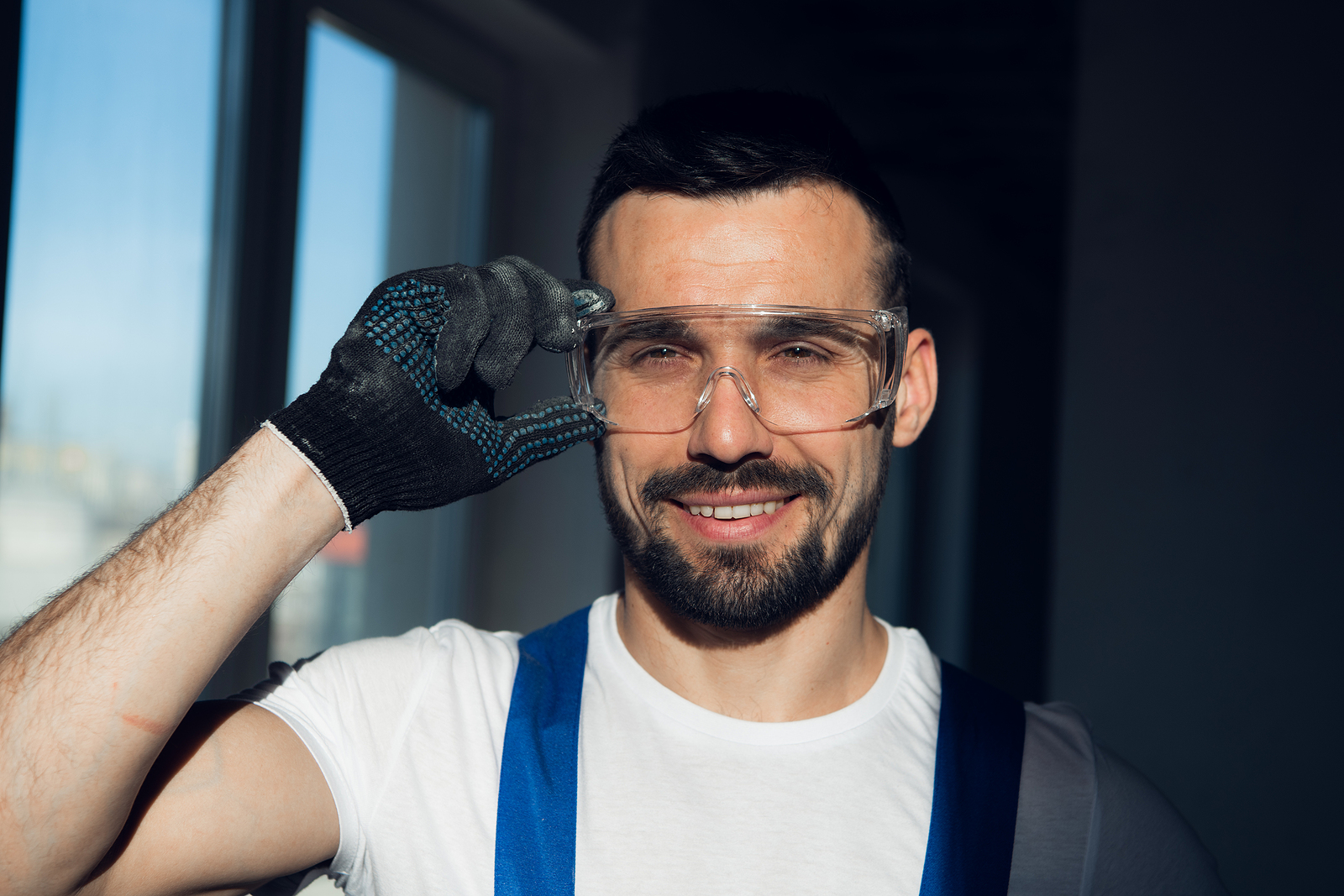
Workplace eye injury can be prevented. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 20,000 eye injuries occur in the workplace each year. Also, these eye injuries cost an estimated $300 million a year in medical treatment, workers’ compensation, and lost productivity. (Johns Hopkins Medicine, 2020)
March is Workplace Eye Wellness Month. Let’s look at common workplace eye injuries and steps to prevent them.
How Does an Eye Injury Occur at the Workplace?
The most common workplace eye injuries are cuts, scrapes, and punctures. They can often happen when workers are handling sharp objects or tools without wearing the appropriate safety gear. Chemical burns, exposure to UV radiation, and foreign objects in the eye are other common causes of workplace eye injuries.
Workplace eye injuries can occur due to flying particles of dust, metal shards, and wood splinters that may fly off during hammering, drilling, grinding and sawing. If objects, like staples, slivers of wood or metal, or nails, go through the eyeball, it could lead to permanent loss of vision. Sometimes large objects may also strike the eye or the face, causing blunt force trauma to the eye socket or eyeball.
Effects of Digital Eye Strain
One of the many adverse effects of the COVID-19 pandemic was increased digital screen time for remote workers. Digital eye strain is also called computer vision syndrome. It is a group of eye and vision-related problems that result from the prolonged use of cell phones, computers, tablets, or e-readers.
Some common symptoms of digital eye strain are dry eyes, blurred vision, burning, tired or itchy eyes, and headaches. Here are some steps to prevent the effects of digital eye strain,
- Sit on a comfortable chair and keep the screen at least 20 to 26 inches away from your eyes.
- Adjust the lighting to lower glare and harsh reflections.
- Use computer glasses with yellow-tinted lenses or anti-reflective lenses. These lenses can increase contrast and block blue light from digital devices.
- Follow the 20-20-20 rule by looking away from the screen at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds, every 20 minutes.
(Prevent Blindness, 2021)
How to Prevent Workplace Eye Injuries
The two primary reasons behind workplace injuries are that the workers were not wearing proper eye protection or wearing the wrong kind of protection for the job. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), workers must use eye and face protection whenever there is a reasonable probability of injury that could be prevented by such equipment. (AOA.org)
It’s also essential for workplaces to recognize their responsibility in keeping their workers safe and healthy to work productively without any distractions. There are several factors to keep in mind when choosing eye protection. Some of them are the nature and extent of the hazard, any other protective equipment in use, the circumstances of exposure, and the personal vision needs of the employee.
Workplaces should provide employees with proper safety equipment such as goggles, safety glasses, face shields, or respirators to reduce the risks of workplace injury. Eye protection should be comfortable and provide adequate coverage. It should fit the needs of the individual and allow for good peripheral vision.
First Aid in Case of an Emergency
If there is a particle in the eye, do not rub the eye. Try to let tears wash the speck out. If the particle does not wash out, keep the eye closed and seek medical care. In case of a blow to the eye, gently place a plastic bag with crushed ice or apply a cold compress without putting any pressure on the eye.
If the eye injury involves chemicals, flush the eye with clean water for at least 15 minutes. Remove contact lenses immediately before flushing the eye if you’re wearing them. Don’t bandage the eye or neutralize the chemical with any other substance.
If there is pain, blurred vision, or vision loss following an eye injury, seek medical attention as soon as possible. (AOA.org)
Experts and doctors believe proper eye protection can reduce the severity or prevent 90% of these eye injuries. Workplace eye injuries are preventable, but only if appropriate precautions are taken.
Workers Compensation for Workplace Eye Injury
Workers Compensation requires proper reporting to be sure the patient is properly diagnosed and treated in compliance with workers comp laws. Our medical professionals are trained to deal with workplace eye injury and can help properly document and set a course for treatment for an employee. You can be assured that our physicians and staff have been trained and will provide the best possible course of action.
Works Cited
Johns Hopkins Medicine. “Study Highlights the Need for Workplace Eye Safety Awareness.” Johns Hopkins Medicine, 2020, clinicalconnection.hopkinsmedicine.org/news/study-highlights-the-need-for-workplace-eye-safety-awareness.
Prevent Blindness. “March Is Workplace Eye Wellness Month.” Prevent Blindness, 25 Feb. 2021, preventblindness.org/march-is-workplace-eye-wellness-month/.
AOA.org. “Protecting Your Eyes at Work.” AOA.org, American Optometric Association, www.aoa.org/healthy-eyes/caring-for-your-eyes/protecting-your-vision?sso=y.